demo
Those suffering from chronic respiratory conditions require special medications to help ease their symptoms. Respiratory diseases, especially asthma, require special medical devices to reduce pain during asthma attacks.
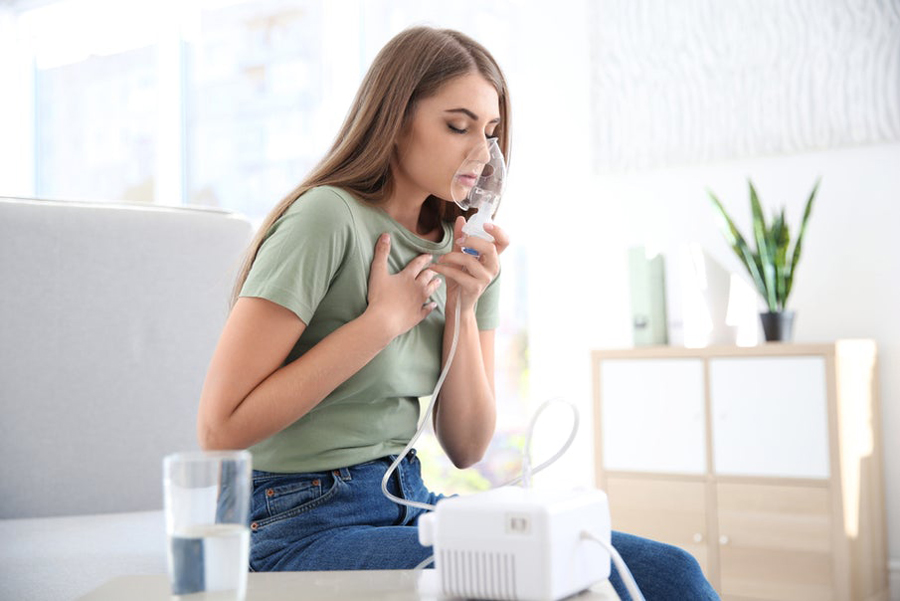
One such piece of medical equipment is a nebulizer. A nebulizer is a medical device used by persons with asthma and other related respiratory conditions to affect the quick administration of medicine into the lungs directly.
The device turns the medicine into mists that can be inhaled through the mouthpiece or face mask. Unlike when the patient directly takes the medication, the device ensures that the medication goes directly in the respiratory system where it is needed.
The device comes in either a battery-run or electric version. Nebulizer comes in a portable size allowing the patient to carry around easily. It also comes in a large size that can either be plugged on the wall or placed on the table. However, the large-sized devices only come in electric forms.
How To Choose Most Effective Nebulizer For Your Condition
If you have breathing difficulties, you must seek prompt medical attention from the doctor. Once you are diagnosed with a respiratory condition, the physician will most likely take you through the most appropriate treatment options for your situation.
There is a higher chance that your doctor will recommend a nebulizer, especially portable nebulizers. The portable devices are always convenient and appropriate for the treatment of a variety of respiratory illnesses. Besides, they help you control your symptoms with much ease.
Types Of Nebulizers
There exist three main types of nebulizers. Before choosing any of the three types, ensure you consult your doctor to identify the appropriate one for your condition. They include:
- Jet: Makes aerosol through compressed gasses
- Ultrasonic: Uses high-frequency vibrations to make aerosol
- Mesh: Forms aerosol as liquids pass through a fine mesh
Conditions Treated By Nebulizers
Individuals with respiratory conditions require effective medication to help ease their symptoms. In most cases, to help treat the medical conditions effectively, a nebulizer might be prescribed to the patient. But what are the conditions likely to be treated by nebulizers?
Let’s explore this in detail.

1. Asthma
Asthma is the most common respiratory condition affecting close to 25 million Americans. Persons with asthma, especially those with severe asthma, regularly experience life-threatening asthma attacks.
To effectively manage and control the symptoms, the patient typically requires nebulizers to administer asthma medications into the respiratory system directly. One of the most common asthma medications used with nebulizers is the inhaled corticosteroids. These medications help reduce inflammation in the airways, leading to reduced chest tightness and breathlessness.
Additionally, nebulizers will help prevent asthma attacks from occurring and also asthma symptoms from increasing.
2. Bronchitis
Bronchitis is another common respiratory condition that is caused by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes. The inflammation of the airways leads to chest tightness, shortness of breath, and fever. Nebulizers help treat the condition as it is used to administer albuterol medications into the lungs to dilate the bronchial tubes. This makes drastically improves your breathing.
3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic lung disease that causes inflammation of the lungs leading to coughing, breathing difficulties, and wheezing. The treatment of COPD requires a combination of various medications, including beta-agonists, anticholinergics, and corticosteroids.
To effectively administer a variety of these medications all at once, one will need a nebulizer as it is the most convenient way to complete your prescribed treatment. If administered daily, the symptoms of COPD will substantially improve, leading to improved health outcomes.
4. Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a life-threatening condition that affects both the respiratory and digestive systems. The human body produces sticky mucus that might block the pancreas and clog the lungs. A cystic fibrosis treatment plan aims to help increase the functioning of the lung through various inhaled medications.
We all know the nebulizer devices can be effectively used to administer several combinations of medicines to the body at once. Besides, the device is invaluable to the patients since it can easily be cleaned to help keep germs.
Common Medications Delivered By Nebulisers
As earlier mentioned, nebulizers can be effectively used to administers different types of medications into the human respiratory system. These classes of medication include:
- Antibiotic: Antibiotics are prescribed to patients with respiratory conditions to help treat and prevent lung infections.
- Bronchodilators: Bronchodilators are a class of drugs used to open up the lung airways, enabling you to breathe with lots of ease.
- Hypertonic Saline Solution: These medications are administered into the respiratory system to help loosen mucus clogged in the lung airways, eventually making it easier to cough.
How To Use Nebulizer
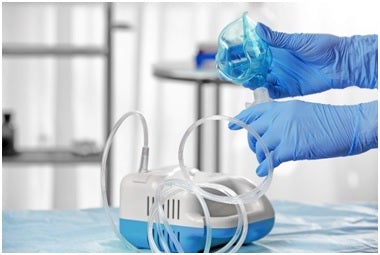
Once a doctor prescribes the use of a nebulizer to help treat your respiratory condition, he/she will provide specific instructions on how to use the device. Despite that, nebulizers generally come with a manual that gives a step-by-step guide on how the device is used. This article explores some of the general instructions on how to use the device.
Firstly, you need to gather all the necessary supplies, which include:
- Medication
- Air compressor
- Compressor tubing
- Mouthpiece or mask
- Nebulizer cup
Once you have assembled all your supplies, follow the following steps:
- Place the air compressor on a flat surface, and then plug it into an electrical outlet
- Check to confirm whether all the pieces of the device are clean
- Wash your hands, especially with soapy water, and dry them
- Place the premixed medications into the container. In case the medication isn’t mixed, mix them appropriately before placing them into the container
- Connect the aerosol compressor tubing and the nebulizer cup
- Turn the compressor on, and ensure that it is misting
- Put the mask or the mouthpiece in your mouth. Ensure you close your mouth to avoid gaps
- Slowly breath in and out to ensure the medication settles into the lung airways
- Continue the breathing in and out until all the medication is gone. This might take roughly less than 15 minutes
In case you still have breathing difficulties after using the nebulizer, inform your doctor.
Maintaining And Cleaning Nebulizers
Nebulizers must always be cleaned and disinfected after use. If the device isn’t cleaned appropriately, germs and bacteria could grow inside it, which might be hazardous if used.
Additionally, you need to regularly replace the tubing since it can’t be cleaned efficiently like other pieces. Here are the general guidelines on how to clean your nebulizer:
- Wash your hands and dry them thoroughly. Ensure you are working on a clean surface
- Disconnect the mouthpiece or masks, tube, medical container, and wash them with clean soapy water
- Leave the pieces to air dry on a clean towel
Leave the pieces to air dry on a clean towel
- Disconnect the detachable parts
- Soak them in the disinfecting solution provided by the doctor
- Soak the parts for close to an hour
- Remove the parts from the solution and let them dry
You must follow the above instructions on how to clean and disinfect your nebulizer. Besides, it would be best to replace some pieces of the devices at least three times a year. Please note that sharing the device is highly prohibited as it might lead to further respiratory infections.
Storing The Nebulizer
- Always cover the nebulizer with a clean cloth if not in use
- Avoid putting the air compressor on the floor. Always place it on flat raised surfaces
- The medication should be stored in a cool, dry place or refrigerator, depending on the doctor’s instructions
- Remove the parts from the solution and let them dry
Advantages Of Nebulizers
- Nebulizers are easy to use
- The device allows for the delivery of multiple medications at once
- Nebulizers are convenient to use with young children
- It offers q quick and convenient way of improving symptoms
- Treatments delivered through nebulizers work faster
Disadvantages Of Nebulizers
- Nebulizers, especially large-sized ones, are not always easy to transport compared to inhalers
- The devices require a stationary power source since most of them are electric
Nebulizer Vs. Inhaler
It is without a doubt that nebulizers and inhalers serve a common purpose. To this effect, the two devices have similarities. For instance, they both serve to deliver medications directly into the lungs to ensure easier breathing. Despite the similarity, nebulizers and inhalers have some vital differences.
- Nebulizers are more convenient and easier to use with young children, unlike inhalers, which are more familiar to adults
- Nebulizers take a little longer to deliver medicines to the lungs than inhalers, which takes roughly less than 5 minutes
- Nebulizers are bulkier, making them harder to carry around. On the other hand, inhalers come in small sizes, thus highly portable
- Nebulizers are relatively expensive compared to inhalers. Additionally, nebulizers are much easier to use
In Summary
Nebulizers are medical devices used to deliver medication directly into the human respiratory system. The device functions to open the lung airways to ensure that you can breathe easily.
Unlike the common inhalers, the device is easier to use and allows for multiple medications delivery at a time. Even though the device is invaluable to persons with respiratory conditions, the device might be hazardous if not maintained well.
Average Lung AirPhysio
ENJOY BETTER BREATHING - Use this 100% Drug Free Device - AIRPHYSIO
Recent Posts
Sports AirPhysio
IMPROVE YOUR SPORTING PERFORMANCE - Use this 100% Drug Free Device - AIRPHYSIO

AirPhysio Child
BETTER BREATHING FOR YOUR CHILD - Use this 100% Drug Free Device - AIRPHYSIO

Categories
- asthma (2)
- atelectasis (2)
- bronchiectasis (2)
- copd (3)
- cystic-fibrosis (45)
- featured (10)
- uncategorized (2)


